Have you ever clicked an ad on a website, landing on the Advertiser’s page, and wondered about the background workings of these ads? Or, have you ever found it irritating to see the same ad repeatedly while watching your favorite movie or web series on an OTT platform, but become curious about how Programmatic Advertising operates?
By 2025, over 90% of digital ads are expected to be purchased through programmatic advertising. Businesses and brands invest a significant portion of their yearly budget to promote their products and services to their target audiences. Today, programmatic advertising is essential for marketers and advertisers as it simplifies getting their brand in front of consumers cost-effectively and timelessly.
What is Programmatic Advertising:
Programmatic advertising refers to the automated buying and selling of digital ads or advertising space in real-time, utilizing software and algorithms across various ad exchanges, Demand-Side Platforms (DSPs), Supply-Side Platforms (SSPs), and Real-Time Bidding (RTB). With the internet’s expansion and technological advancements, advertisers can now efficiently bid for ad spaces and precisely target specific audiences

What is Advertiser:
An advertiser refers to a brand or company that allocates a substantial part of its annual budget to advertising. The goal is to present its product or service to a targeted audience—defined by demographics, interests, or consumer behaviors—ultimately reaching a wide consumer base, fostering brand loyalty, and boosting sales.
Examples of Advertisers: Nike, BMW, American Airlines, Indigo, Ford, etc.
What is Publisher:
A publisher refers to either an individual or a company that generates content on its platform, aiming to attract and engage an audience. Publishers always strive to create high-quality content.
Examples of publishers include websites, mobile applications, YouTube, Facebook, Instagram, and OTT platforms.
What is Advertising agency:
Advertising agencies are independent companies that provide services to clients and get paid for the services they provide. The ultimate goal of ad agencies is to execute, manage, and optimize the campaigns so that the campaigns reach the client’s expectations and KPI’s.
Core Components of Programmatic Advertising: DSPs, SSPs, Ad Exchanges, RTB, DMP, Audience/Data and Ad Server Explained:
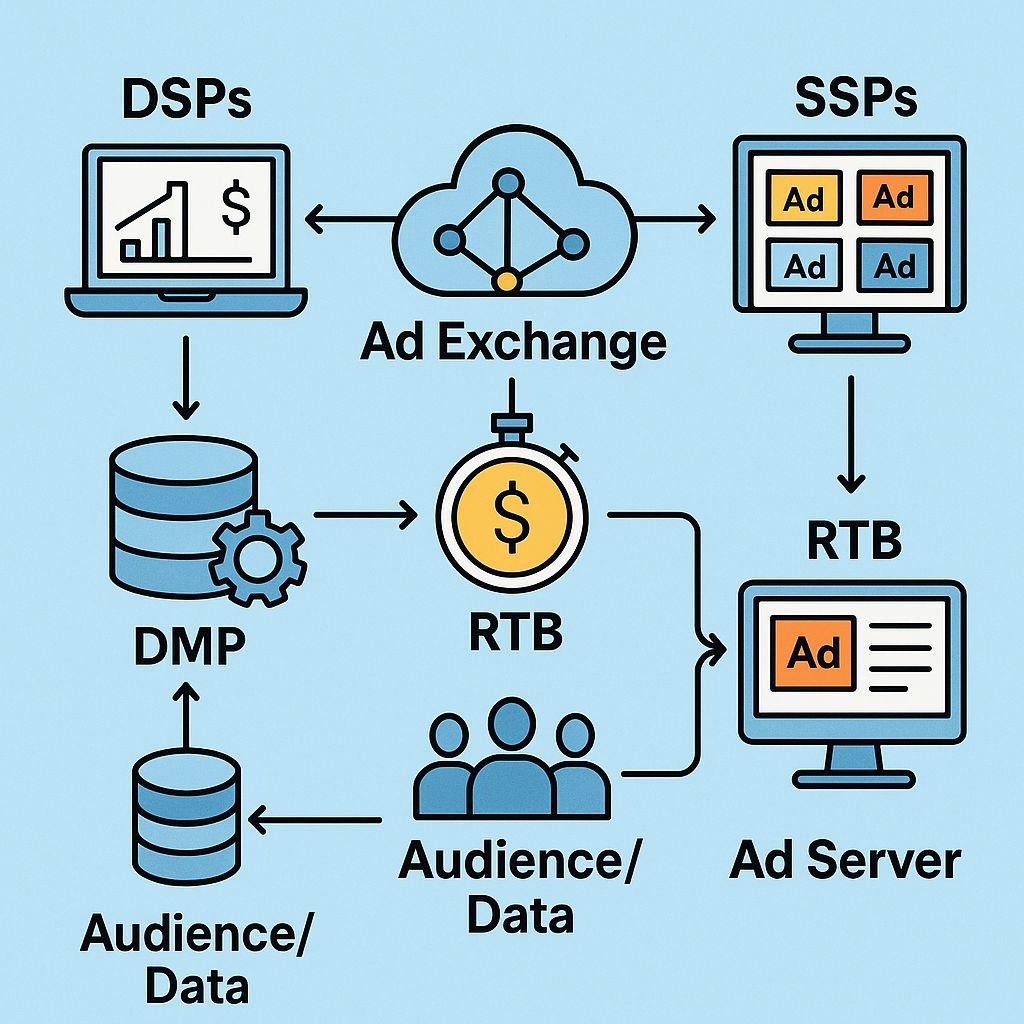
Basics of Demand-Side Platforms(DSP):
A demand-side platform (DSP) is a programmatic advertising technology platform that allows advertisers and media buyers to purchase digital ad inventory from multiple ad exchanges and SSPs automatically through Real-time bidding on an impression-by-impression basis(CPM).
How advertisers use DSPs:
Advertisers and Ad agencies use DSP to set up their ad campaigns by targeting specific audiences based on their demographics, geo, behaviour, and controlling bids and the budget. It also helps us to analyze the performance of the campaigns in real-time by pulling the campaign reports from the DSP and making the best optimizations to reach the campaign goals.
Examples: DV360, The Trade Desk, Xandr, Amazon DSP, Yahoo DSP.
SSP (Supply-Side Platform) Explained:
A supply-side platform (SSP) is a Programmatic Advertising technology platform designed to help digital media owners and publishers manage, sell, and optimize their available ad inventory on multiple ad exchanges, ad networks, and DSPs to maximize publishers’ revenue for their ad space in an automated, secure, and efficient way.
How publishers use SSPs to manage ad inventory:
Publishers or media owners first connect their websites or apps to the SSP platform, then SSP shows the available ad inventory in real time, and it will be accessed by multiple ad exchanges and DSPs. Now the advertiser who wants to promote their product or services by running advertising campaigns can bid on these available ad inventory(ad slots on a website) through real-time bidding (RTB).
There are multiple advertisers that bid for these specific ad slots, but the advertiser who bids high will win the auction, and SSP automatically selects that advertiser and displays their ad to the user on the website or app. Here publishers can control pricing of the ad slots, with specific ad formats, and set rules for which advertisers can access their ad inventory. So publishers can earn revenue for each impression without manual effort and maximize their revenue.
Examples: Magnite, PubMatic
What are Ad Exchanges:
An ad exchange is a technological platform that acts as a mediator between the advertiser and publisher, and it helps advertisers with the process of buying ad space and helps publishers with the process of selling ad space. The ad exchange sits in the middle and facilitates the transaction between both advertisers and publishers in real time.
Examples: OpenX, MoPub, AppNexus, Index Exchange, Rubicon Project, Smaato, SmartyAds, PubMatic, Google AdX.
Types of Auctions in Ad Exchanges: There are two main types: open exchanges and private marketplaces (PMPs).
Open Exchange vs Private Marketplace:
1. An open exchange is a public digital marketplace with a list of advertisers and publishers. Multiple advertisers can bid on available ad inventory or ad slots from a wide range of publishers through real-time auctions and can get broad reach to build awareness of the brand, but with less control over where ads appear. In Open exchange, advertisers do not have access to buy the premium inventory from specific publishers
2. Private marketplace: The advertisers are ready to bid high and get access to most premium inventory from the publishers. So the brands ad will be shown in a premium website that has a high number of users. Publishers have more control over who can buy their ad space, ensuring better brand safety and ad quality.
How Real-Time Bidding (RTB) Powers Programmatic Ad Buying:
The RTB is a programmatic auction process where publishers can sell their ad slots and advertisers can buy the ad impressions in milliseconds. The highest bidder’s ad is instantly shown to the user when a user loads a webpage on a website or app.
DMP (Data Management Platform):
A DMP is a platform that collects huge volumes of data from different digital and offline sources, organizes and analyzes them. DMPs help advertisers and publishers segment audiences for better targeting.
DMP Examples: Adobe Audience Manager, Lotame, Oracle’s Bluekai.
A DMP collects three types of data:
1. First-Party Data: First-party data is the most valuable data that a brand collects from its own website users or website visitors. This data is valuable because it comes directly from people who have interacted with the brand, giving marketers insights into their preferences and behaviors.
Examples of first-party data include website analytics, email lists, and customer purchase history.
2. Second-Party Data: A brand collects its own users’ data from the website or apps and sells it to the other brand. It is often acquired through partnerships with non-competing companies that have similar target audiences.
Examples of second-party data include customer data shared between an airline and a car rental company or between a hotel and a travel booking site.
3. Third-Party Data: Third-party data is collected by companies that specialize in data collection and aggregation, rather than directly by the brand or its partners. This data can be sourced from a variety of online and offline channels and is often sold in segments based on demographics, interests, and other criteria.
Examples of third-party data include demographic information such as age, gender, Household income, and browsing behavior of the user when they stay on a web page.
What is an Ad Server:
An ad server is a platform that makes decisions about what type of ad should be shown to a user, and when to show the ad. It collects and reports the data of users based on certain metrics such as impressions, clicks, etc.
Examples: Google Ad Manager, TTD, Sizmek, DV360, Adroll
How Does Programmatic Advertising Work?
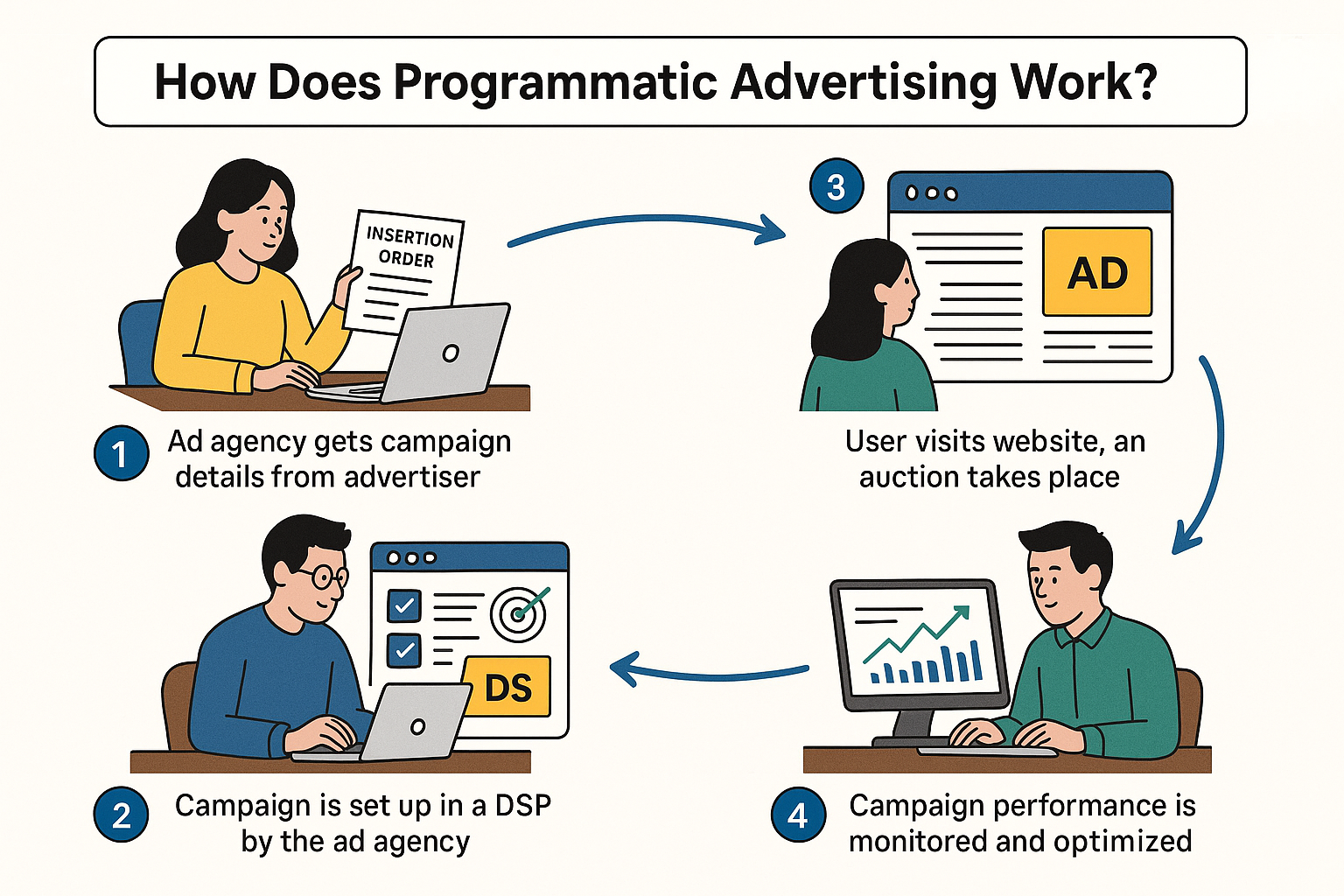
1. Ad agencies get the campaign details such as campaign flights, CPM, Imps budget, flight budget, Geo, campaign strategy, and other targeting parameters from the advertisers.
2. Ad campaigns can be created in Demand-Side Platform with specific targeting parameters, set a budget, flights, control bids, and assign creatives.
3. When a user visits a website, a real-time auction is triggered in the webpage. This way, the campaign created by campaign managers starts showing their ads on the websites.
4. Campaign managers continuously monitor the campaigns and make sure to deliver the imps/budget daily till the end of the campaign. They monitor both delivery and performance of the campaigns to make sure they hit the campaign KPI goals.
Conclusion:
Programmatic advertising has completely transformed the way digital ads are bought and sold. As more brands shift towards data-driven advertising, learning how programmatic works will give you a competitive edge in the industry. It’s not just about automation—it’s about making smarter, faster, and more effective decisions.


